The next series of CUCM APIs you will experiment with in Python are all part of a collection of APIs known as the UC Serviceability XML API that expose multiple capabilities for CUCM administrators to automate management and monitoring tasks.
For your reference, the family of UC Serviceability XML APIs consist of the following 5 APIs:
Each of these APIs has its own dedicated WSDL file that describes its unique methods (service endpoints) and unlike AXL (AXLAPI.wsdl) they are available to download directly from a given CUCM server. Note that all methods (service endpoints) are NOT available in all CUCM releases. See https://developer.cisco.com/site/sxml/discover/overview/ for more information.
Let's take a closer look at the RisPort70 and Perfmon APIs with a sample Python script.
The tasks you will accomplish in this section are:
Follow these steps to perform the above listed tasks:
 at left, and you see a list of folders and files.
at left, and you see a list of folders and files.
The RisPort API allows you to query CUCM for the real-time state of registered devices. This is different than AXL which provides you with the static database configuration of devices. With the RisPort API you can retrieve information such as registration status, IP address, running firmware load, and more. To retrieve this data you will use the selectCmDevice method of the RisPort API as shown below.
The values above indicate that you want to retrieve any kind of device, any model of device (255 means any model), devices that are in any status (Registered, Unregistered, etc...), registered to any node in the cluster, registered using any protocol (SCCP or SIP), and select the devices whose description starts with the word "Cisco".
The XML below shows what the expected SOAP request to CUCM should look like. As before, you do not have to manually create this XML body. Zeep will take care of doing this for you.
To pass the selection criteria to the RisPort API, first create the following variable that you will use to pass as an argument to selectCmDevice method. Paste the following into your file. Once you click anywhere in list of "RUN AND DEBUG" configurations, You should see a predefined Configuration for running a python
script named Python: soap_sxml.py in the list. Make sure it is selected:
Once you click anywhere in list of "RUN AND DEBUG" configurations, You should see a predefined Configuration for running a python
script named Python: soap_sxml.py in the list. Make sure it is selected:
 .
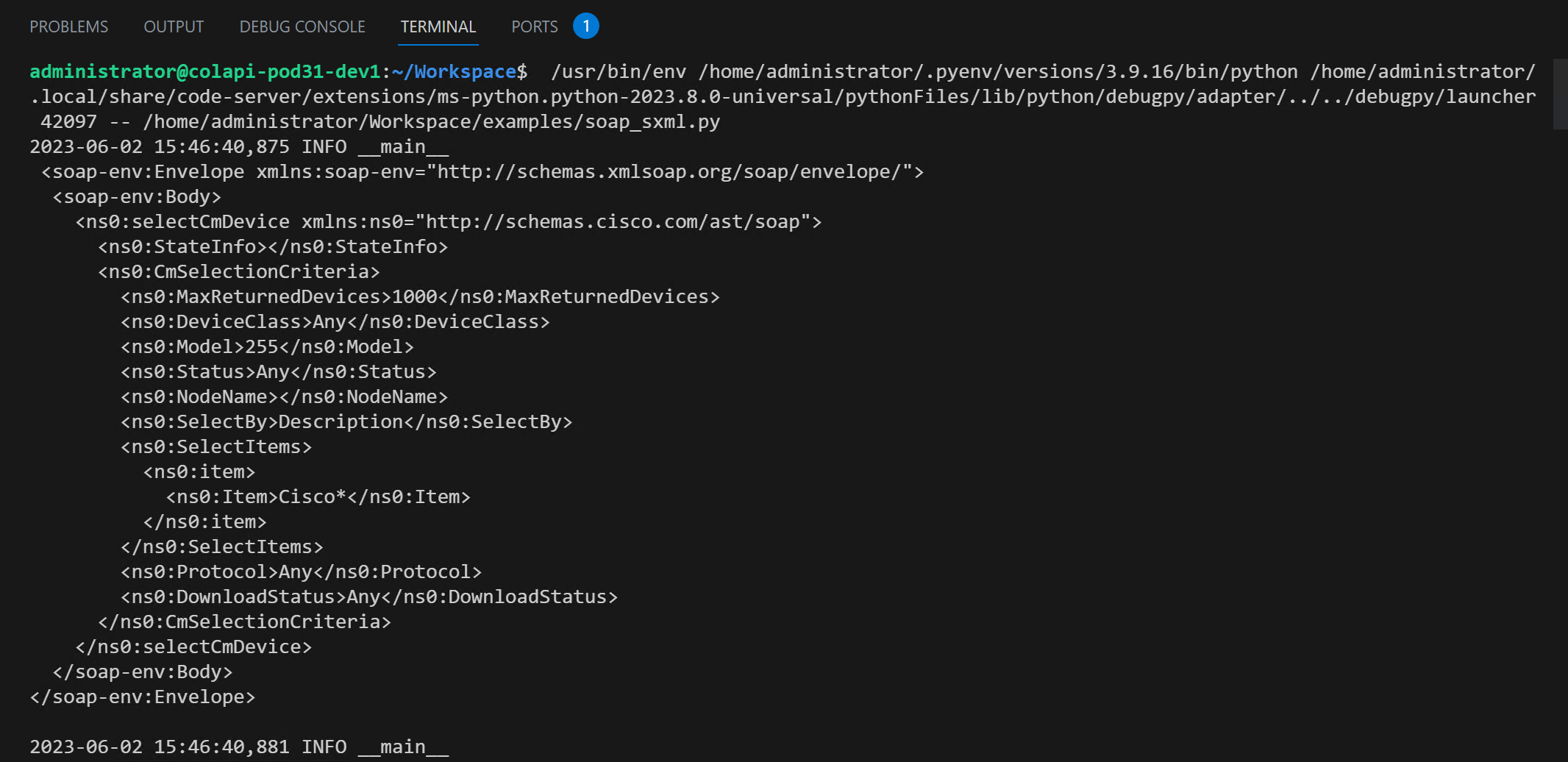
Upon running the soap_sxml.py Python script a new Python Debug Console terminal window will open at the bottom
where the output of the script will be displayed. The screenshot below only covers the outbound SOAP payload sent to CUCM.
There should be more logging output than what is shown in the screenshot below.
.
Upon running the soap_sxml.py Python script a new Python Debug Console terminal window will open at the bottom
where the output of the script will be displayed. The screenshot below only covers the outbound SOAP payload sent to CUCM.
There should be more logging output than what is shown in the screenshot below.
 The selectCmDevice response parsed by the zeep library looks as follows. The output is quite large since you are retrieving all
device details from the RIS DB. For your reference please find a trimmed output of phone_query_response below. Your console output
should look slightly different but should show the CSFPOD5UCMUSER device in a registered state.
The selectCmDevice response parsed by the zeep library looks as follows. The output is quite large since you are retrieving all
device details from the RIS DB. For your reference please find a trimmed output of phone_query_response below. Your console output
should look slightly different but should show the CSFPOD5UCMUSER device in a registered state.
In the previous step, you used the RisPort70 serviceability API to query the RIS DB for devices that matched a specific selection criteria. Next you will use the PerfMon API to query a simple set of CUCM Performance counters. If you are unfamiliar with PerfMon, it is a service available on all CUCM servers to provide real-time counters for the various services running on the server. These metrics include everything from CPU and memory utilization to number of registered devices and active calls. PerfMon has a series of objects which are logical groupings of related counters. Counters provide a single metric related to the object. For example, the Cisco CallManager object contains a variety of counters related to the Cisco CallManager service such as registered phones, active calls, and the uptime of the service. An easy way to browse the various objects and counters available is by using the Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT).
 Once you click anywhere in list of "RUN AND DEBUG" configurations, You should see a predefined Configuration for running a python
script named Python: soap_sxml.py in the list. Make sure it is selected:
Once you click anywhere in list of "RUN AND DEBUG" configurations, You should see a predefined Configuration for running a python
script named Python: soap_sxml.py in the list. Make sure it is selected:

 .
Upon running the soap_sxml.py Python script a new Python Debug Console terminal window will open at the bottom
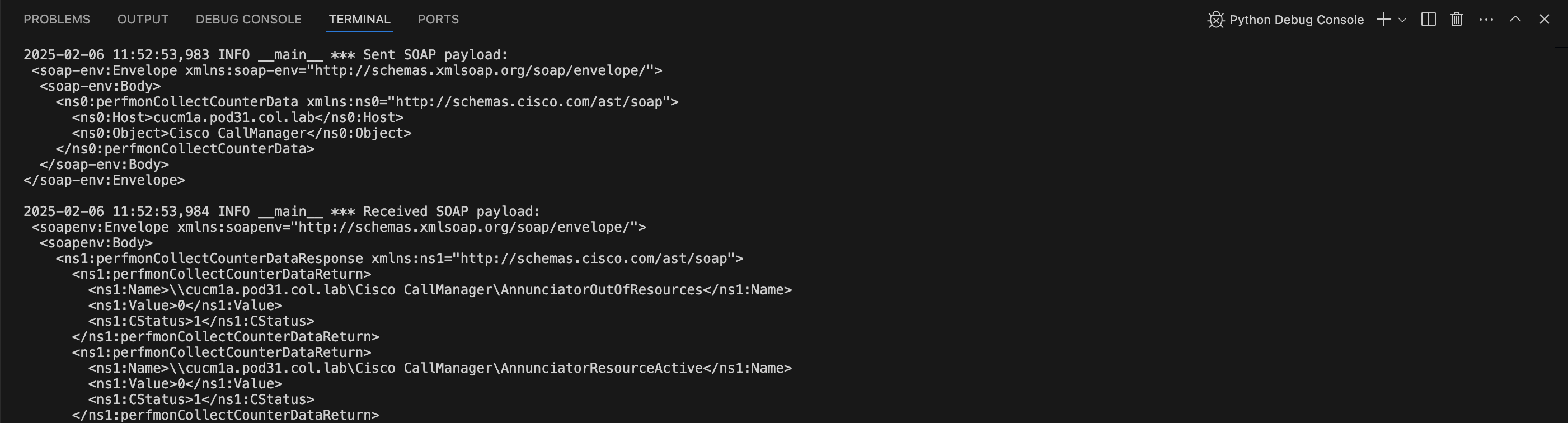
where the output of the script will be displayed. The screenshot below only covers the outbound SOAP payload sent to CUCM
for the perfmonCollectCounterData request, there should be a lot more logging output than what is shown in the screenshot below.
.
Upon running the soap_sxml.py Python script a new Python Debug Console terminal window will open at the bottom
where the output of the script will be displayed. The screenshot below only covers the outbound SOAP payload sent to CUCM
for the perfmonCollectCounterData request, there should be a lot more logging output than what is shown in the screenshot below.
 The perfmon_query_response response parsed by the zeep library should look similar to the output below.
The output is quite large since you are retrieving all
PerfMon Counters for the "Cisco CallManager" class. For your reference please find a trimmed output of perfmon_query_response.
The perfmon_query_response response parsed by the zeep library should look similar to the output below.
The output is quite large since you are retrieving all
PerfMon Counters for the "Cisco CallManager" class. For your reference please find a trimmed output of perfmon_query_response.
The method of using the PerfMon API highlighted above is the simplest use of the API. Most use cases involve continuously querying the same performance counters at a certain time interval and storing them, perhaps as a time-series in a database of some kind. To do this, the PerfMon API provides a mechanism by which you open a session, add counters to that session, then periodically collect session data for those counters. For more information on the more advanced usage, reference the PerfMon API Reference and look at how to use the perfMonOpenSession, perfMonAddCounter, and perfMonCollectSessionData methods.
You have now completed both the AXL and Serviceability XML APIs examples with Python. In the next section you will be introduced to REST-based APIs.